TB 9-6625-2308-35
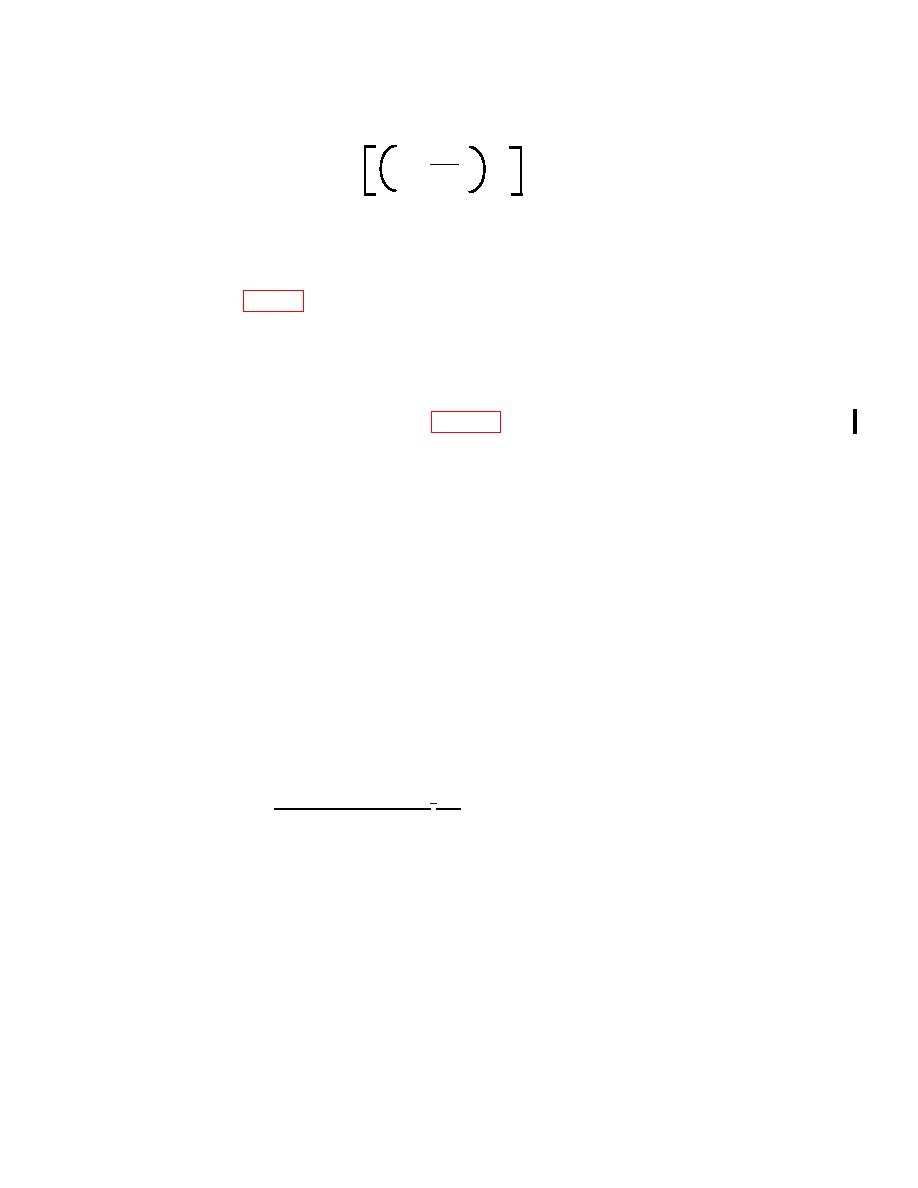
R1/R2
x 100
-1
Linearity Error (%) =
(P1/P2)
Accumulated linearity error (%) = the sum of the current linearity error and the previous
accumulated linearity error.
(19) The linearity error (%) and accumulated linearity error (%) will be within the
limits specified in table 3.
b. Adjustments. No adjustments can be made.
13. Power Sensor CALFAC
a. Performance Check
(1) Connect equipment as shown in figure 2, except remove low pass filter.
(2) Set the step attenuator to 70 dB. Connect TI sensor to TI front panel
CALIBRATOR output and zero the TI by pressing ZERO/CAL.
(3) Set the step attenuator to 0 dB after the TI chimes to signal completing the
zeroing process. Reconnect sensor to equipment hook up.
(4) Set the multimeter to a range that results in a 1 V resolution. Connect the
positive and negative leads to the VCOMP and VRF connectors respectively on the rear panel
of the power meter.
(5) Fine zero the power meter and set power meter RANGE switch to 1 mW.
(6) Record the multimeter indication as V0.
(7) Set the signal generator output to 1.0 GHz and level to 1.00 mW as indicated on
the power meter.
panel of the power meter and connect it to chassis ground. Record this voltage as VCOMP.
(10) Calculate that actual power using the formula listed below and record as Pt .
2VCOMP (V1-V0) +V02-V12
Pt =
4R (CALIBRATION FACTOR)
Where:
Pt =
Actual incident power
VCOMP =
value recorded in (9) above
V1 =
value recorded in (8) above
V0 =
value recorded in (6) above
R=
value recorded in 7 d above (≈ 200 Ω)
CALIBRATION FACTOR =
value of thermistor mount at 50 MHz
CHANGE 1 11


