TB 9-6625-187-24
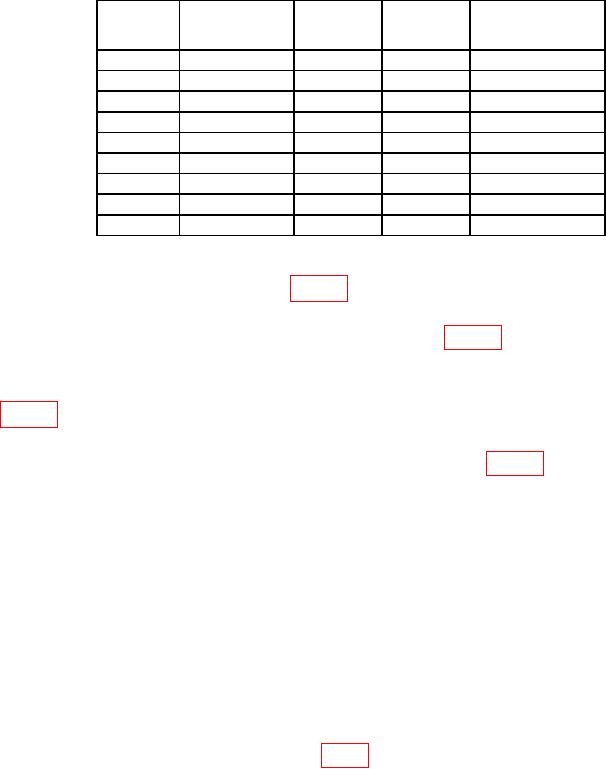
Table 5. Adjustment with Power Range Switch Set to 15.
RF Power Meter
Correction TI reading1
Low Pass
Reading
level
(MHz)
Filter
Factor
(watts)
80
TLC125-6EF1
25
TLC30-4EF7
50
TLC75-6EF1
N/A
150
TLC200-6EF1
12.5
N/A
225
TLC316-6EF1
12.5
N/A
400
TLC450-6EF1
12.5
N/A
405
TLC450-6EF1
12.5
N/A
800
TLS1225-5EF1
12.5
N/A
1000
TLS1225-5EF1
12.5
Use correction factor to determine actual TI reading below 100 MHz.
1
(10) Turn RF power on and slowly adjust the output power until the TI settles and
matches the TI reading level listed in table 5.
(11) Once the TI reading is stable at the value in the TI reading level column, record
the RF Power Meter reading in the appropriate column of table 5.
(12) Reduce RF power to minimum and set source to standby.
(13) Repeat steps (9) through (12) above for the remaining frequencies listed in
(14) Determine the single highest value and the single lowest value readings from
the recorded values in RF Power Meter reading column in table 5 and add those two
numbers together.
(15) Take the sum of the two numbers added in step (14) above, then divide by 2 and
record; this will be used as the average value for use in other steps.
(16) With RF source in standby, set the Signal generator to 100 MHz and change the
Low Pass Filter to TLC125-6EF1.
CAUTION
Do not allow RF Power Amplifier output to exceed the TI
Power range switch setting selected.
(17) Divide 156.25 by the average value recorded in step (15) above and record the
quotient. Slowly increase RF power output at 100 MHz until the Power Meter reads the
same as this quotient and remains stable.
(18) Adjust TI potentiometer R9 (fig. 2) until TI meter indicates 12.5 watts; wait
several minutes for stabilization before proceeding.
(19) Reduce RF power to minimum and set source to standby.
(20) Set the TI Power range switch to 5.

